PRP and Cell Treatments
Everything you need to knowPRP and Cell Treatments
The tissues used for regeneration and rejuvenation in plastic surgery are the epidermis and dermis layers of the skin and the fibroblast cells of the fatty tissue and connective tissue.

What is cell therapy?
The use of these tissues, which are the body's own building blocks, has been used successfully for years in order to eliminate losses in the functions of the skin, which is the main working material of plastic surgery, as well as subcutaneous connective and fatty tissues, and even muscles, tendons, vessels and nerves. Therefore, with this application, which means healing with one's own tissue, we are protected from risks such as tissue rejection and infection, which we encounter in applications made from another donor. On the other hand, the substances called growth factors contained in these transferred tissues will stimulate the renewal (regeneration) and rejuvenation of the relevant tissues. will be at the event.
The tissues used for regeneration and rejuvenation in plastic surgery are the epidermis and dermis layers of the skin and the fibroblast cells of the fatty tissue and connective tissue. In addition to these, blood-derived platelet-rich plasma (PRP, platelet-rich plasma), thrombin and fibrin are products used for these purposes. An even more advanced treatment product is stem cell treatments . Gene therapies, which are still experimental in cancer treatments and in some cases have reached semi-clinical levels, offer great promise in the near future.
Another aspect of cellular therapies is tissue engineering products. These laboratory-derived products aim to replace the body's missing tissues, and to date, significant success has been achieved in areas such as the ear, larynx (larynx), veins, tendons and contractile muscle tissue. However, studies are still ongoing for the routine use of these products. Another dimension of these studies is biological printers. In the coming years, treatments with biological printers and nanotechnology robots may enter clinical practice in terms of cellular repair of tissues.
What is stem cell?
Stem cells are cells that reside in tissues and are in a silent state, with the potential to turn into the needed tissue cell when necessary. There are two types: embryonal and adult type stem cells. Adult stem cells consist of cells that can be found in many tissues and there are no strict restrictions on their use, other than the regulatory restrictions described in the previous paragraph. Embryonal stem cell is the cell obtained from the inner cell mass of the structure that will form the baby in the womb and has undergone many divisions.
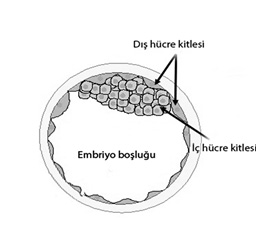
Image Note: Embryonal stem cells are located in the inner cell mass in the cross-section of the embryo.
These have the ability to transform into many more tissue types than adult stem cells. Although stem cells are portrayed as miraculous treatments due to consumption pollution in the field of healthcare, it is often not possible to obtain perfect results for every patient, from repair to aesthetic applications in clinical applications. For example, although regional stem cell injections and skin patches have a healing effect in the treatment of wounds that occur in underlying chronic diseases such as diabetes, it is not possible to prevent new wounds from appearing after a few months in diabetes, which is a permanent disease. Because the damage to the vessels and nerves is permanent and unless prevented. It will create problems.
Although the regeneration and rejuvenation effects of stem cells have long been demonstrated in experimental and clinical studies, their permanence is controversial.
The main areas of use of stem cells in plastic surgery can be divided into two groups. The first group consists of repair-based surgeries such as reconstruction and repair of chronic wounds, burns, severe injuries, nerve and tendon damage, and breast reconstruction after cancer surgery. The second group includes aesthetic surgery applications . Stem cell applications are widely used as auxiliary methods in aesthetic surgery to improve skin and soft tissue quality . As emphasized, it should only be considered as an auxiliary method. Because, for example, on the elderly face, a superior result compared to standard plastic surgery operations has not yet been achieved in single applications. Another question mark is the amount of stem cells given and the frequency of application. If the number of cells per cubic centimeter is above or below a certain level, there is a possibility that the patient will not benefit from the application. Again, it is not recommended to repeat stem cell injections earlier than 15 days after the maximum dose. Therefore, our patients should discuss the results with their doctors in detail.
Where are adult type stem cells obtained?
Although stem cell sources vary widely, three basic sources are used in plastic surgery:
- blood,
- bone marrow,
- fat tissue.
The types of stem cells obtained from these tissues may also vary. Blood and bone marrow derived stem cells are called hematopoietic stem cells (HSC). These cells have the ability to transform into various blood elements. In clinical practice, the highest number of HSCs can be obtained from the bone marrow. For this purpose, a sufficient amount of stem cells can be obtained by entering the anterior protrusion of the pelvis and the shin bone, called tibia in children, with special tools called trephine.
Adipose tissue is another important tissue as a source of stem cells. Among the fat tissue-derived stem cells, we mostly use the mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) type in plastic surgery practice. MSCs are cells that have the potential to transform into various connective tissue elements. To date, the effectiveness of MSCs has been demonstrated in many experimental and clinical studies for purposes such as wound healing, tendon, bone, muscle, vessel and nerve healing. It is possible to obtain mesenchymal stem cells from fat tissue, which can be found in large amounts in the body.
Can stem cells be injected immediately after collection?
Stem cells must be purified in blood or fat tissue products obtained through various means. For this purpose, the tissue taken is subjected to enzymatic, chemical or mechanical purification and is made ready for injection. While these purification processes can be partially carried out in operating room conditions with special mini stations, the most ideal is to purify in GMP certified (Goog Manufacturing Practice / Good Manufacturing Conditions) laboratories specially designed for this job. Again, in clinical applications where the obtained stem cells are required to be passaged and propagated following special permissions from the ministry, the only authorized institutions are GMP certified laboratories (4).
Am I really being treated with stem cells?
Stem cell therapy is one of the applications that is claimed to be performed today but is not performed frequently. Of course, I'm talking about illegal practices here. While most patients are informed in these centers, not much information is generally given about the equipment and kits used in the procedure. In the more well-intentioned of these centers, at least platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection is applied as stem cells, but serious infections can be encountered even with PRP in patients who do not receive closed system application. Therefore, get information from your doctor about how the stem cells are obtained to ensure that PRP is not used instead of stem cell application. If necessary, ask about the kit brands used and their certificates of conformity.
What are platelet-rich plasma, thrombin and fibrin?
The basic elements of blood are blood cells and plasma. The blood is rotated with high-speed centrifuge devices and the cellular elements are precipitated, leaving a part called plasma at the top. In the part of the plasma close to the blood elements, there are dense cells called platelets that enable blood clotting. Therefore, this part is called platelet-rich plasma (PRP). The cellular elements in PRP contain various substances called growth factors, and these have the activity of providing rejuvenation and regeneration, which are the main goals of cellular therapy. In order for PRP to be injectable into humans, blood must be obtained in pure form by passing it through special closed kits after centrifugation.
PRP treatment is applied as an adjunct to reconstruction and repair or aesthetic surgery with the same requirements as described in the stem cell section. In order for its effects to last in the long term, repeated injections are required at intervals. PRP treatment is used in various areas, from joint diseases to nerve compression, from facial rejuvenation to scars (1-4). We can call PRP injection a type of self-mesotherapy.
Like PRP, thrombin and fibrin are also blood products, and both are substances in the blood clotting chain. It has been shown that thrombin and fibrin increase the adhesion of skin patches applied to open wounds, and they are used successfully in clinical practice. Fibrin is used especially in bleeding coagulation disorders and unstoppable bleeding.
After the PRP is first centrifuged in special tubes, there is plasma at the top, platelet-rich layer (PRP) below it, and a yellowish-white white blood cell-platelet mixture layer called buffy coat at the bottom. At the bottom is the red layer, which is rich in red blood cells. After the bottom red layer is withdrawn from the tube with special pipettes, centrifugation is repeated and the precipitation process is applied once more, and the PRP and buffy coat are also removed, the remaining layer is called platelet-poor plasma (PPP). PPP also has various uses for rejuvenation purposes.
Image Note: By subjecting your blood sample to a high-speed spinning process called centrifugation in special systems, blood cells and plasma are separated into layers.
Are there any restrictions on the use of cellular products?
As with all therapeutic products, there are widely accepted international restrictions on the use of cellular therapies. First of all, the production of these products can be carried out at two separate points. The first one is sterile operating room conditions, and if the tissues to be removed will not be subjected to advanced biological processes and will not be used outside the basic function of the tissue from which it is taken (homologous tissue), it falls into this class and does not require special permission from the ministries. On the other hand, there are non-homologous tissue applications, in which the tissue taken is used for a purpose other than its normal function by going through special processes in closed systems (enzymatic hydrolysis, passage propagation, etc.), and in this case, the approval of the Ministry of Health is required for the application. This last type of cell treatments are carried out in laboratories with special ventilation and disinfection conditions called GMP laboratories. There are 6 GMP laboratories in our country.
Your doctor will give you the most appropriate information regarding the need for ministry permission in practice.
Embryonic stem cell applications are banned in our country and many other countries due to their potential harm to the embryo due to unethical practices in various countries.
In order to prevent infections that may occur in cellular treatments, the most basic restriction is the production of the tissue to be taken and used in closed systems without contact with the external environment. For example, if a blood product is to be used in practice, the type of blood taken should never be opened and must be passed through closed systems during transfer.
What is fibroblast injection?
Fibroblasts are cells that are widely found in our body and form the basis of connective tissue. They synthesize and secrete collagen-type proteins, which are the basic elements of connective tissue, and various growth factors. Fibroblasts are cells that can be produced and multiplied in GMP-certified laboratories in recent years. It has become a frequently used treatment to restore skin elasticity and increase connective tissue support in the aging body. For this purpose, a skin biopsy is generally taken from behind the ear with a 3mm circular blade called a punch and sent to the GMP laboratory in special equipment. Fibroblasts, which are cultured in the laboratory and produced in approximately 1 month, are then delivered to the physician who will perform the application in an injectable form. The biopsy procedure, performed with local anesthesia (regional anesthesia), is quite simple (5).
Fibroblast injection is produced individually and therefore the possibility of allergy is very low. It does not create an appearance that will cause a change in facial expression. It provides a long-lasting solution and has no tendency to escape into tissues far from the area where it is ejected. It is a method that can be applied for smoother, tighter skin. Applications are planned as three sessions, 2-3 weeks apart.
Main uses for fibroblast injection:
- removing facial wrinkles,
- elimination of spots and dark areas,
- filling acne pits,
- treatment of wounds and burn scars,
- giving volume to the lips,
- As an auxiliary treatment in hair restoration,
- in the treatment of gum diseases in dentistry,
can be used. The effect is generally reported to be approximately 1-4 years after the second session.
The fibroblast suspension is treated with substances such as gentamicin, penicillin and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to minimize protection during the production process. Patients who are allergic to any of these ingredients should report this prior to administration. In such a case, cancellation of the application may be on the agenda.
Resources:
- Bousnaki M, Koidis P. Platelet-rich plasma for the therapeutic management of temporomandibular joint disorders: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017 Oct 20.
- Abdel Aal AM, Ibrahim IM, Sami NA, Abdel Kareem IM. Evaluation of autologous platelet-rich plasma plus ablative carbon dioxide fractional laser in the treatment of acne scars. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2017 Aug 30:1-8.
- Marck RE, Gardien KL, Stekelenburg CM, Vehmeijer M, Baas D, Tuinebreijer WE, Breederveld RS, Middelkoop E. The application of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of deep dermal burns: A randomized, double-blind, intra-patient controlled study Wound Repair Regen. 2016 Jul;24(4):712-20.
- Liu J, Ren J, Su L, Cheng S, Zhou J, Ye X, Dong Y, Sun S, Qi F, Liu Z, Pleat J, Zhai H, Zhu N. Human adipose tissue-derived stem cells inhibit the activity of keloid fibroblasts and fibrosis in a keloid model by paracrine signaling. Burns. 2017 Oct 10. pii: S0305-4179(17)30472-2.
- Itaya T, Hirai T, Hirai T, Numoto H, Takeda H, Ueda M. The Use of Fibroblasts for Ameliorating Structural Changes Associated with Skin Aging. Rejuvenation Res. 2017 Oct;20(5):383-388.
"Health is the most important thing you have in life!"
Contact us now to schedule an appointment.

