Department Detail
Learn more about our departmentsHair Transplant
Hair Care, Hair Mesotherapy, Hair Physiology, FUE Method Hair Transplantation
Although it varies in different areas of the body, the scalp is an organ consisting of terminal hair follicles that contain color (pigment).
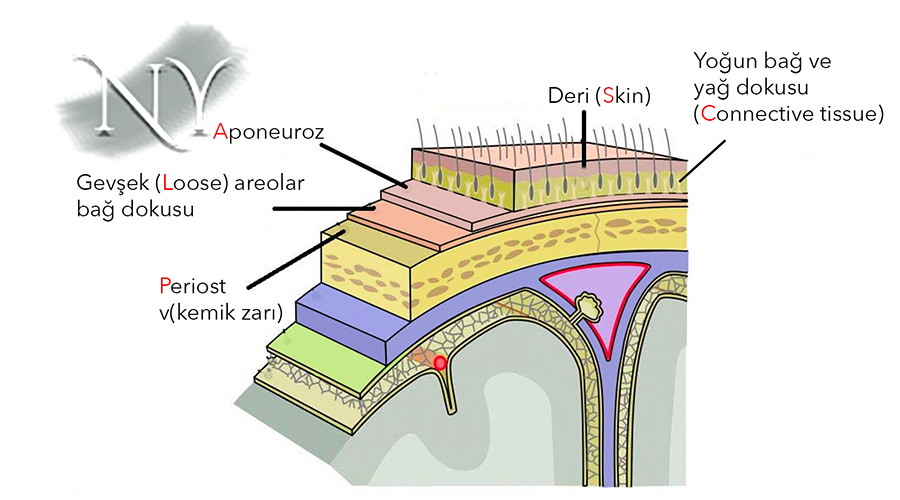
The scalp is the name given to the scalp , and it is an abbreviation consisting of the first letters of five different words in English. ( skin , connective tissue, a poneurotic tissue (galea aponeurotica; connective tissue that forms a bridge between the muscles in the forehead and nape region), loose areolar tissue (loose connective tissue; allows the scalp to slide over the bone), periosteum (or pericranium).
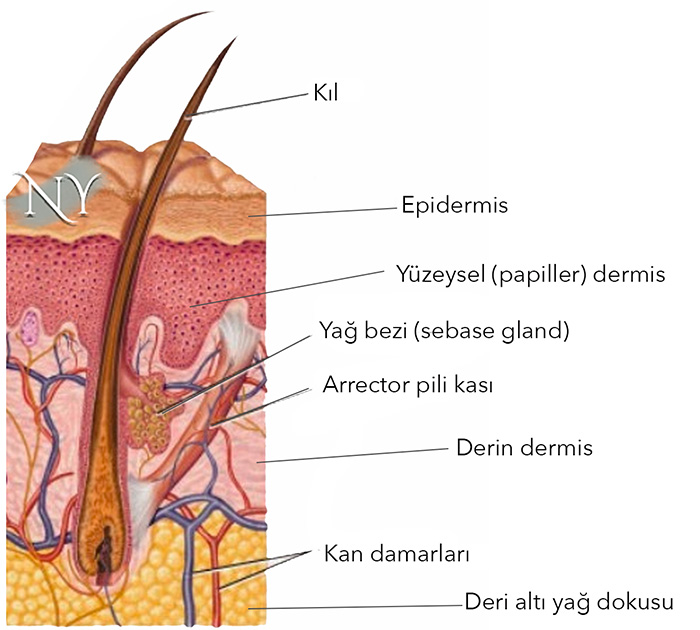
The hair shaft consists of the root or hair bulb embedded in the skin and the hair shaft which is free. The root contains sweat and oil glands which produce the oil and sweat needed to prevent the skin from drying out. There are muscles called arrector pili between the skin and the hair root which contract when the autonomic nervous system activity (cold, heat, excitement etc.) and cause the hair shaft to stand up.
The hair covering the skin on the skull, along with the beard and moustache area, is the only structure that is attempted to be reproduced, unlike other hair-bearding areas on the body. There are three basic periods in the physiological growth and development of hair. This basic period is actually similar to the growth, development and death process of any cell. Each hair root experiences this process at certain intervals and eventually sheds the hair inside it and enters the hair growth and development cycle again to grow new hair. Since this three-period process is different for each hair root, thinning is not observed in healthy hair and a normal scalp continues on its way with an average of 80 hair roots shedding per day.
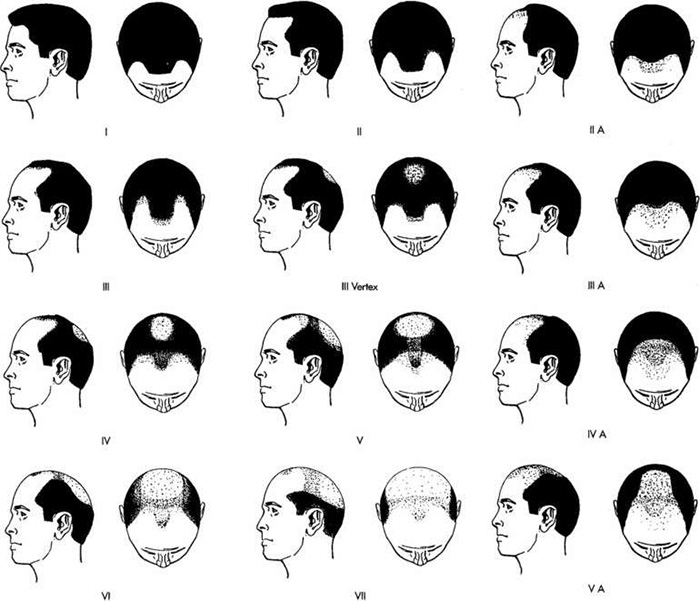
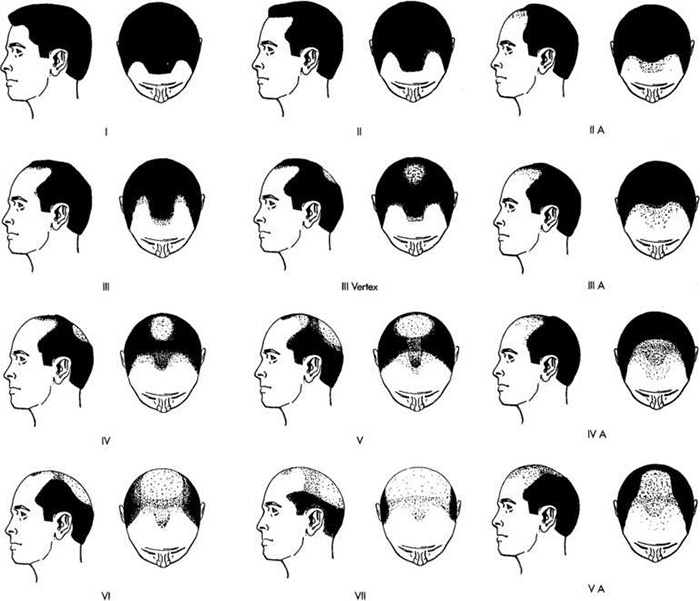
Image Note: Classification by Norwood in 1975.
The anagen phase is the main growth and cell proliferation phase of the hair. It lasts approximately 3-5 years and varies between races. For example, in Asians it can grow up to 7 years and at the end of this period the hair can reach a size of 1 meter. Similarly, it is known that hair growth is faster at night because the anagen phase is more active at night.
Telogen phase is the approximately 10-day intermediate phase in which the hair gradually weakens and becomes ready to fall out.
The catagen phase covers a period of approximately 3 months of silence following the shedding of the hair. After this, the anagen phase is passed again, where cell proliferation increases.
Hair loss is a problem that occurs for different reasons that vary from person to person. There may be an underlying factor (infection, rheumatic skin disease, etc.) or it may occur without any reason at all. Therefore, when the factor is treated in a hair loss that has a factor, the hair can be regained.
Hair health can be affected by metabolic and hormonal problems, infections related to hair, and rheumatic diseases affecting the skin. Therefore, hair loss that starts recently and accelerates suddenly and is concentrated in certain areas should be investigated in terms of these clinical pictures.
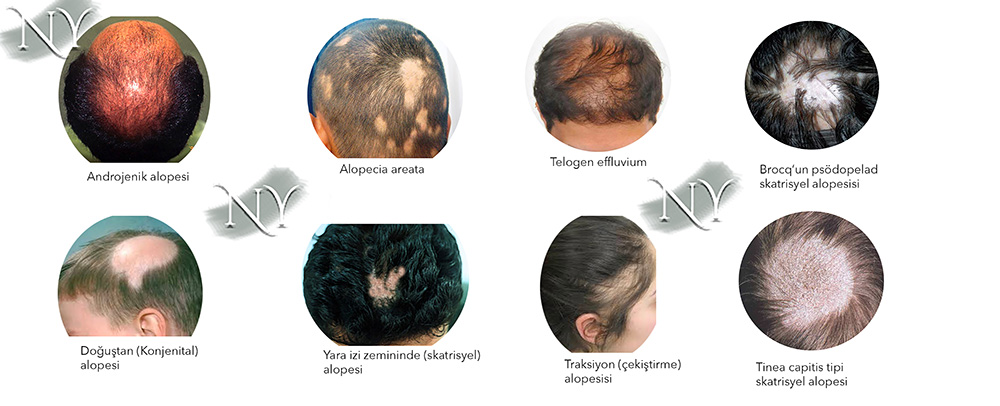
The most common cause of hair loss in both genders, especially in men, is androgenic alopecia.
The hair follicles on the scalp contain receptors for testosterone. Testosterone is an androgen-type male hormone and is secreted from the adrenal gland in women. Testosterone and its metabolite, dihydrotestosterone, cause thinning and shrinkage in the hair follicles. Why does this happen? The area behind the ears and the nape is not affected much in this sense. Androgenic alopecia can start with the forehead and temples in men and progress to the vertex at the back. Sometimes vertex-type peak hair loss can occur together and a hairy area bridge may remain in between. Since hair loss and baldness follow a certain shape (pattern) in the male sex, various classifications have been made to cover mostly men, and the most frequently used of these is the classification first defined by Hamilton in 300 men and then revised by Norwood in 1975 with an evaluation of 1000 men [3,4].
Although medical treatments (such as regional treatments such as minoxidil or testosterone antagonists that penetrate the bloodstream such as finasteride) can be tried, the definitive treatment for androgenic alopecia is hair transplant surgery. Although the results vary from person to person and the quality of the transplant, it is expected that more than 80% of the transplanted hair follicles will take root with an experienced team.
In androgenic alopecia, hair loss starts from the temples in men and spreads towards the vertex of the head, while in women, a more scattered loss is expected. It is related to the testosterone hormone activity in the body. One of the target organs of testosterone is the hair follicles on the scalp. It is a type of hair loss that can have a familial predisposition.
Drug treatment of androgenic alopecia includes drugs such as finasteride, which reduces testosterone hormone activity, and minoxidil, whose mechanism of action is not fully known. The effectiveness of these drugs varies from person to person. Minoxidil is a more commonly used drug and is used morning and evening, and is preferred in 2% spray forms for women and 5% for men. Finasteride can cause sexual dysfunction (mostly reversible problems such as impotence and ejaculation problems) and therefore should be used under the supervision of a doctor. Dudasteride, the more effective and newer form of this drug, is effective on both types of receptors that can cause hair loss. Ketoconazole is a fungicide and its shampoo form has been shown to reduce dandruff and stop hair loss. Its mechanism of action is not fully known. PRP (platelet-rich plasma) is the slightly cloudy part obtained by separating a person's own blood. This part, which contains various growth factors, is precipitated by centrifuging the blood in special glass tubes or kits and is taken into an injector and injected into the area to be applied. Its effectiveness in androgenic alopecia is controversial and there is no study with sufficient clinical evidence level. However, different centers state that PRP injection sessions, especially for hair transplant candidates, will be beneficial in terms of increasing the number of surviving hair follicles in order to prepare the recipient area before the application. Botulinum toxin-A is used in many areas, but it is one of the preparations that have been clinically tested for hair loss in recent years. Freund and Schwartz published the preliminary results of their open-ended study in 2010 (1) and stated that botulinum toxin-A application can reduce hair loss and stimulate hair growth in some men. While the formation of dehydrotestosterone from testosterone, which is responsible for hair loss, is higher in an environment without blood and therefore without oxygen, testosterone is converted more into the hormone called estradiol in well-blooded areas and therefore hair loss may decrease. Botulinum toxin-A is a substance that potentially increases the blood flow of the tissue in the long term (2).
Apart from medication, the most basic treatment for androgenic alopecia is the surgery called hair transplantation. Yes. Hair transplantation is a surgery. It is one of the surgeries that should be emphasized and given serious importance like all other long and tiring surgeries of plastic surgery. The only branch that is qualified for hair transplantation surgery is plastic surgery.
Hair loss can be reversible when there is an underlying cause. Telogen effluvium is this type of hair loss and it is reversible.
Telogen effluvium, the second most common type of hair loss in women after androgenic alopecia, actually includes the physiological hair loss in newborns and hair loss that can be seen during pregnancy and then corrected with the growth of new hair. In addition, it has been observed that telogen effluvium can occur in cases of goiter (under- or over-activity of the thyroid gland), anemia, malnutrition, low-protein diet, heavy diet, and excessive stress. Treatment of these factors with medications and nutritional supplements will mostly provide hair growth. Get information about this treatment from a plastic surgery specialist.
Regional hair loss may occur as a result of fungal infections or rheumatic diseases reflected on the skin. This loss, called alopecia areata, can be stopped with nutritional supplements or treatment directed at the cause, but hair regrowth is not expected.
Alopecia areata, a type of hair loss that starts in a certain area of the hair and spreads in a short time, and causes hair loss in a certain area after a few weeks, can be stopped by treating the underlying cause, but hair growth in the area is not expected. I have had patients who have achieved very good results with platelet-rich plasma (PRP). However, this treatment is still in the trial phase and may not yield positive results in every patient. PRP treatment involves taking the person's own blood, separating it with special systems, and then separating the platelet-rich part and giving it to the diseased area on the person's scalp. Hair mesotherapy can also be effective in the treatment of alopecia areata. Hair transplant surgery can be tried in people who are not effective with any medical treatment. However, before this, it should be confirmed that the underlying disease has completely regressed (remission).
Traction alopecia occurs when excessive tension is applied to the hair, which disrupts blood circulation to the scalp. Once established, hair loss can be permanent.
There are many different reasons that can cause traction alopecia, from hairpins used by children pulling too much on the hair and disrupting blood circulation to the person having a hair pulling disorder. In this case, the constant disruption of blood circulation leads to developmental regression in the hair root in the area and the hair root thinning and falling out over time. Although previously mentioned medical treatment methods can be tried after traction alopecia has settled down, the basic treatment is hair transplantation. Unlike androgenic alopecia, the transplanted hair may fall out again if the patient applies tension again. Therefore, it should be tried on suitable patients. For the health of their hair, please do not tie your children's hair too tightly with hairpins.
There may be congenital deficiencies in certain areas of the scalp. These deficiencies can range from complete skin loss (aplasia cutis congenita) to congenital alopecia, where there is only no hair.
Partial or complete absence of hair from birth is not uncommon. This condition can be seen with various layers of the skin. In this case, depending on the extent of the deficiency detected, the hairless area can be removed at a certain age and the scalp can be brought face to face, or hair transplantation can be applied to the area at a later age. In the anomaly called aplasia cutis, there are usually congenital deficiencies in the skin and may require repair.
One of the most serious problems that cause hair loss is actually deep burns. Burns leave very serious scars and deformed skin. Sometimes it may be necessary to put skin patches. Hair does not grow in the burned area and is known as cicatricial (scar-related) alopecia.
Any element that creates a scar on the scalp actually prevents hair growth in that area. This condition is called cicatricial alopecia. This condition, which can have many metabolic, infectious (bacterial or fungal) or traumatic causes, can be treated with hair transplantation. One of the types of cicatricial alopecia with an unknown cause is the condition defined by Brocq, where hair grows in clumps. There is hairless and poorly nourished skin between these clumps and hair growth is not expected.
In fact, contrary to popular belief, the target result should not be hair growth, but the achievement of healthy hair. Hair health is a subject that requires education in society. Everyone should take care of their hair by knowing the structure of their hair more or less, and every patient who starts to lose hair should definitely go through a doctor's check-up. It should not be forgotten that hair loss can be caused by many preventable reasons when caught early.
Among the medical treatments applied for hair health, mesotherapy has been shown to be particularly beneficial in stopping hair loss, balancing the dryness of the hair and increasing the hair diameter. It is also used to increase the blood flow to the recipient bed before hair transplantation.
Hair mesotherapy, in parallel with other mesotherapy derivatives, first involves increasing regional blood flow with initial sessions and then treatments aimed directly at the target, namely the hair follicle. Although many drug cocktails can be prepared, today they are sold more practically as commercial products. The hair-growing effect of mesotherapy is to stimulate hair follicles that have entered the telogen phase and to stimulate their transition to the anagen phase, but the effects are reversible when the treatment is interrupted for a long time. The same applies to platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatment.
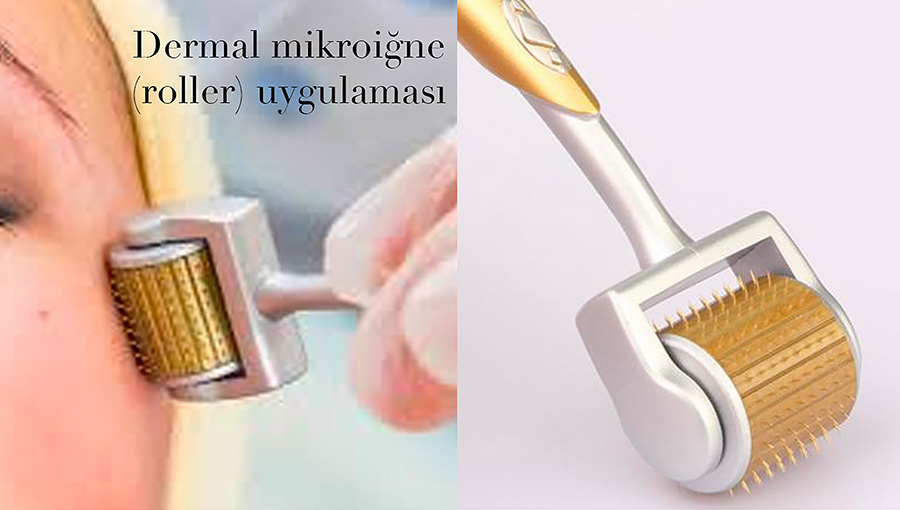
Another application that has become popular recently is micro-needling, which involves scanning the scalp with needle rollers for 8-10 passes.
There are publications showing that the use of this device together with PRP and 5% minoxidil provides a significant increase in the number and diameter of hair follicles in the trichogram after 3-4 sessions and that the amount of hair that can be pulled out in the hair pulling test also shows a significant decrease (5, 6). However, I have not observed any studies on the long-term permanence of these effects.
When medical treatments for hair restoration do not work, two types of surgery within the scope of aesthetic plastic surgery come into play as a solution. These are tissue expander application and hair transplantation surgeries. These surgeries can also be applied to patients who we think will not get results from medical treatments.
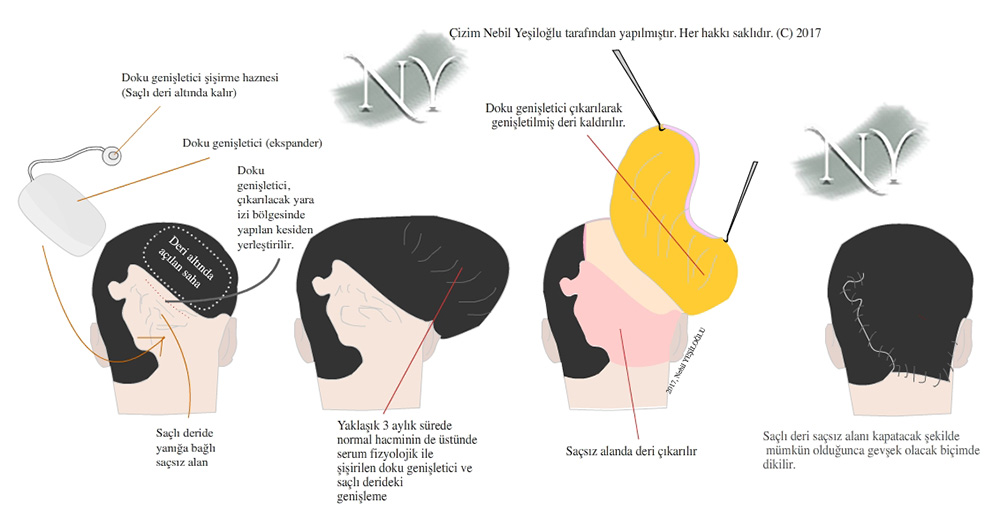
The use of tissue expander balloons in plastic surgery is particularly aimed at replacing unhealthy skin on the healed burn site with healthy skin that has a good blood supply. Again, after breast cancer surgery, permanent silicone prosthesis is placed after the expansion of the existing tissue in order to recreate the breast. Before hair transplantation became widespread in the restoration of hairless areas on the scalp, tissue expander implants were mainly used in patients. Tissue expanders provide flexibility in the scalp and allow it to spread to the hairless area. There is a two-stage surgical process with a 2-3 month interval. In the first, the tissue expander is inserted through an incision made from the hairless area and placed in the pocket created under the scalp. Inflation is applied from the inflation chamber with physiological serum 1-2 times a week to the point where the patient starts experiencing pain. This volume is usually 10-15% of the total volume. I have patients who have inflated up to 15-20% more than the maximum volume until the second session. In the second session, the tissue expander is removed through the incision first and the scalp is released. Depending on the amount of area covered, hairless skin is removed and replaced with hairy skin. Stitches are placed without tension.
The most ideal results for hair transplantation surgery are obtained if there is a healthy recipient bed, a sufficient number of healthy hair patches, and the patient does not have a metabolic disease or a smoking habit.
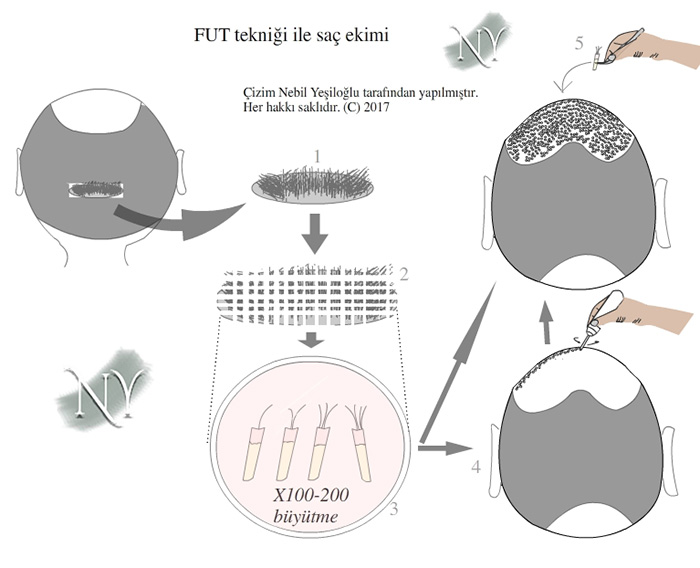
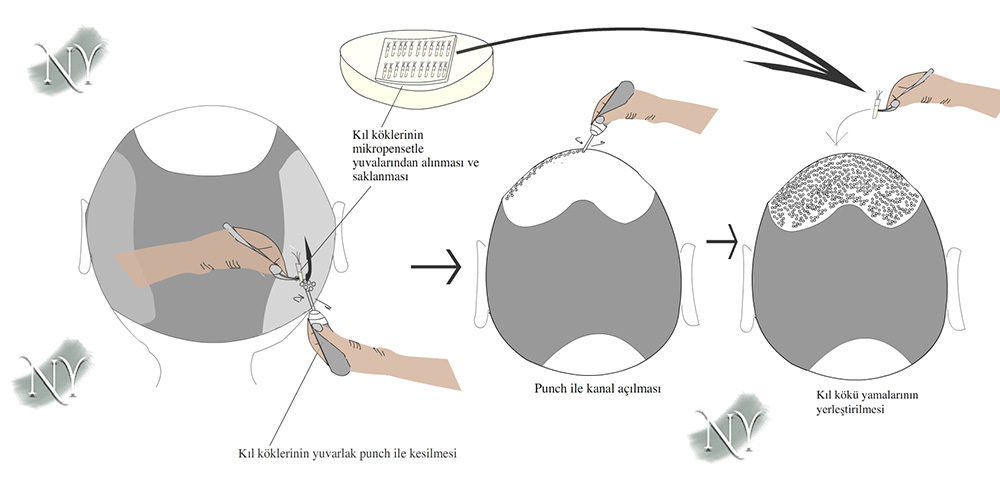
After the first modern hair transplantation technique was defined by American physician Norman Orentreich in 1952, thousands of patients underwent hair transplantation and achieved very successful results. Two basic techniques are used for hair transplantation. In the first technique developed, the follicular unit transplantation (FUT), an extraction of a certain length and width is applied from the hairy skin at the nape of the neck, which is resistant to shedding. These are prepared under the operating microscope in sections containing a number of hair follicles ranging from single to quadruple. The area where the scalp is taken is closed with stitches. During the preparation of the hair follicles, the recipient area where they will be transferred should be prepared and channels are opened here so that the hair can grow at the appropriate angle. Then, the hair follicles are planted in the area in a way that provides a natural hairline. The entire surgery is performed with regional anesthesia. In this technique, only the area where the hair patch will be taken is shaved and since the hairy areas are stitched face to face at the end of the surgery, the part where the hair follicles are taken will be indistinct on the patient.
The second hair transplantation technique, follicular unit extraction (FUE), is a surgical technique in which the hair follicle patches to be taken are extracted one by one and then transplanted into opened channels similar to the FUT technique. Circular blades called punches with a diameter ranging from 0.7 to 3 mm are used here. The punches we use are usually 0.7-0.8 mm in diameter.
In this surgical technique, if the area to be transplanted is large, the patient's entire hair must be shaved with a machine. The shaving-free FUE technique can be used in patients who will undergo limited transplantation. In this technique, the patient is required to have long hair. The hairy area immediately above the area where the hair follicle patch will be taken for transplantation is protected, and only the area where the patch will be taken is shaved and this is hidden with the protected hair on top.
Hair transplantation surgery is a long operation, part of the operation is done in the face down position and the rest in the supine position. This long operation can sometimes be divided into two-day sessions.
It should not be forgotten that hair transplantation is, first and foremost, an operation and that this operation should be performed by a team managed by an aesthetic plastic surgery specialist. Hair transplants performed by non-physicians in so-called under-the-counter hair transplant centers can result in disappointment that can lead to widespread scalp loss.
Hair transplant surgery is not a surgery that causes excessive blood loss. During the surgery, bleeding is limited by applying a special bandage to the head after regional anesthesia.
Before hair transplant surgery, which is one of the long-lasting surgeries of plastic surgery, such as 5-9 hours, please stop taking blood thinners (aspirin, plavix, xarelto, etc.) if you are using them, starting from the date your doctor warns you. Similarly, smoking disrupts tissue blood flow, and will negatively affect the nutrition of the transplanted hair patches. Therefore, quit smoking at least 1 week before and after the surgery.
Regardless of the technique used in hair transplant surgery, you will be given some suggestions for post-operative care. Paying attention to these suggestions can make the results of the surgery much more pleasing.
I do not want you to wash your hair for the first 3 days after hair transplant surgery. This is important for the process of hair follicles sticking to their place. In some centers, the channels where the hair will be transplanted are opened narrowly and the recipient area may vomit the placed patch. If the hair patches appear to have overflown at the end of the surgery, washing can be postponed until the 4th or 5th day.
The first wash after the hair transplant surgery is performed by the hair transplant team after the 3rd day and you will be told how and with which materials hair care will be applied afterwards.
After the hair transplant, you should wash your hair with special lotions and soft touches for a while. Never use a blow dryer or curling iron type devices after washing. These devices burn the hair roots and cause rapid shedding.
By the end of the first week after the hair transplant, the crusts formed in the transplanted areas should be shed. Inform your doctor if the crust lasts longer than a week. Long crusting periods may negatively affect new hair development. After the crusts are shed, you can perform the hair care prescribed for you.
After hair transplantation surgery, do not enter areas such as pools, sea and solariums for the first 10-15 days. Chemical and infectious pollutants that may be in pools and seas can damage hair follicle patches. If solarium and sunbathing are to be applied, I recommend special hats.
In the first days of hair transplantation surgery, a special bandage is applied to prevent excessive swelling around your face. Despite this, there may be widespread swelling around the face and especially around the eyelids. Please get advice from your doctor about this.
Any blows to the head after hair transplant surgery will negatively affect your recovery. Therefore, if possible, limit your sports activities to minimize the possibility of possible blows.
After hair transplantation, the transplanted hair follicle patches go into telogen and catagen phases for a while. In other words, they fall out and it may take an average of 6-12 months for them to grow back and the hair diameter to thicken.
Anemia is a common problem in the development of all tissues, and it is also an important parameter in hair transplantation. Therefore, maneuvers that accelerate the duration of surgery continue to be developed. In order to minimize the effects of anemia, hair root patches are separated and kept on pads impregnated with a special solution at temperatures between 4-10 degrees. After transplantation, the response of the hair root patch to anemia is a silent transition to the catagen period. During this process, the hair root falls out and a new one begins to grow from below. The first hair strands that grow are thin but thicken over time. Mesotherapy can also be useful after hair transplantation in order to shorten the duration of this normal catagen response. Therefore, the loss of transplanted hair should not worry you.
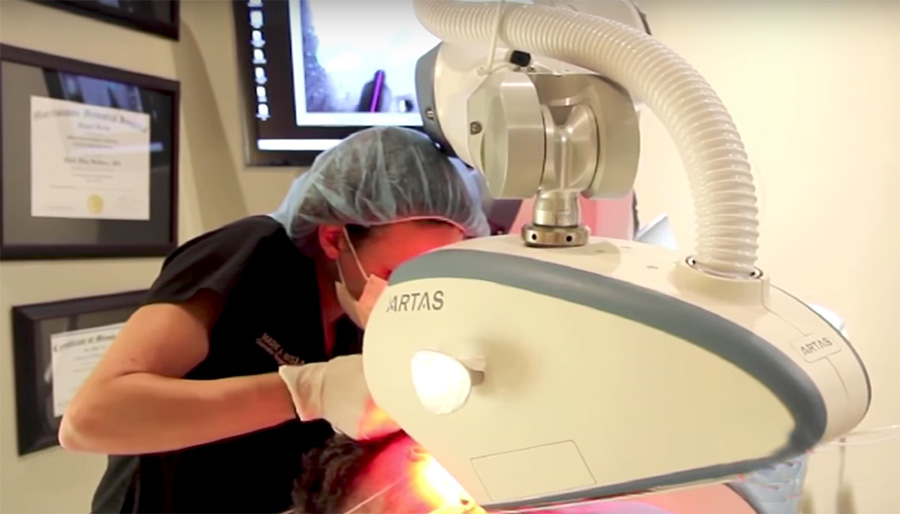
Robotic hair transplantation has recently gained commercial significance, especially in the USA, with approvals from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Robotic surgery has become popular in many areas and has also started to be used in hair transplantation surgeries to reduce the energy and time spent. First, a mechanism that takes photographs and calculates the correct angle has been attached to the cutting head used to obtain the hair root patches taken with a technology called NeoGraft at a more appropriate angle without damaging them. This system again requires a surgeon. The robot used in a second system called ARTAS prepares the hair patches to be planted with its own punch blade and only then a surgeon is needed to extract the hair root from the ground. The robot also provides the channel opening in the recipient area for the patches taken at the appropriate angle and then the transplant is performed.
Another problem with these technologies is that the punch blades that can be used are much larger in diameter than normal hair transplant punches. This causes the prepared hair patches to be larger in volume.
The complications that may occur after hair transplantation surgery can be quite significant.
As in every surgery, the most classic problems I can say after hair transplant surgery are wound area infection and blood accumulation under the skin. Especially when disinfection and sterilization rules are not followed sufficiently, serious infections that can be life-threatening can be encountered. Infections that may occur during hair transplant surgery can create serious skin abscesses that can also lead to hair loss in the area. There may even be losses from the skin. For this reason, hair transplantation should only be performed by aesthetic plastic surgery specialists who are experts in the field. Because when the mentioned problems occur, the only competent branch to solve them is plastic surgery.
Blood accumulation (hematoma) under the wound line can be seen especially in patients who do not stop taking blood thinners, and it can also rarely occur in those who do not use any medication. In this last group, a bleeding focus (hematoma) can occur when a circular knife called a punch injures a deep vein. This hematoma should be drained with regional anesthesia.
Hair not growing can be seen more frequently in teams that have not completed the learning curve, have high rates of root damage while taking the hair root patch, and place the hair root patch at inappropriate angles and narrower channels than necessary. As I mentioned before, opening a narrow channel causes the hair root to be ejected from the channel. Some automatic hair root placers, in particular, place the patch directly by just dipping into the scalp, and this can be a more common problem.
Unnatural hairlines and angles are caused by improper planning and the wrong number of hair follicles placed in the wrong area. Treatment of an improper hairline is not easy, especially when it is very prominent in the forehead area, and may require surgery.
Sources:
- Freund BJ, Schwartz M. Treatment of male pattern baldness with botulinum toxin: a pilot study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010 Nov;126(5):246e-248e.
- Temiz G, Yeşiloğlu N, Şirinoğlu H, Akpınar AC, Sarıcı M, Filinte D, Filinte GT, Bozkurt M. Increasing the survival of transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous flaps with a Botulinum toxin-A injection: A comparison of surgical and chemical flap delay methods . J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016 Jul;69(7):944-51
- Hamilton JB. Patterned loss of hair in man: Types and incidence. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1951;53:708–28.
- Norwood OT. Male pattern baldness: Classification and incidence. South Med J. 1975;68:1359–65.
- Bao L, Gong L, Guo M, Liu T, Shi A, Zong H, Xu X, Chen H, Gao X, Li Y. Randomized trial of electrodynamic microneedle combined with 5% minoxidil topical solution for the treatment of Chinese male Androgenetic alopecia. . J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2017 Oct 13.
- Jha AK, Udayan UK, Roy PK, Amar AKJ, Chaudhary RKP. Original article: Plateletrich plasma with microneedling in androgenetic alopecia along with dermoscopic pre and posttreatment evaluation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2017 Aug 3. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12394. [Epub ahead of print]