Breast Reconstruction, Breast Repair, Breast Reconstruction After Breast Cancer
Everything you need to knowBreast Reconstruction, Breast Repair, Breast Reconstruction After Breast Cancer
breast reconstruction, breast repair, breast reconstruction after breast cancer, silicone breast reconstruction, breast reconstruction from hip skin, breast reconstruction from back skin, breast reconstruction from abdominal skin
 https://www.youtube.com/embed/ZZ7ECRg27UY?rel=0&autoplay=1&showinfo=0
https://www.youtube.com/embed/ZZ7ECRg27UY?rel=0&autoplay=1&showinfo=0The breast , which is an important self-organ for women , may be lost for various congenital and acquired reasons. First of all, I want my patients to understand that the organ in question is the "breast" and not the breast. Among the gender-determining secondary character organs that have been constantly tried to be suppressed in society, unfortunately, the breast is one of the organs that has been hit the hardest in this sense. So much so that in some primitive tribes, they still try to stop the development of the breast by applying a tight bandage to the rib cage from the beginning of puberty. Just like in female circumcision, an attempt is made to prevent the woman's satisfaction in sexual intercourse by cutting off the clitoris.
The absence of breasts in the female body initiates a process that starts with a lack of self-confidence, leads to severe depression, and eventually leads to withdrawing from social life and becoming withdrawn. Many psychological analysis studies on this subject have shown that the absence or removal of the breast can cause serious psychological problems, at least as much as our severable limbs such as hands, fingers and legs (1-5). For this reason, every year October is known as "breast awareness month" in order to explain the dramatic consequences of this to people who have lost their breasts or who were born without breasts and that they do not need to endure them. Turkish Plastic Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery Association organizes many events for this purpose.
Image note: The absence of breasts can lead to a process that starts with serious self-confidence problems and ends with depression.
Instead of providing information divided into sections on this page, I will try to convey the subject through frequently asked questions about breast reconstruction and reconstruction. [These questions were compiled from your e-mails and mutual conversations. Please read carefully.]
I don't have breast cancer. But I only have one nipple from birth. Why might my breasts not be developed?
In plastic reconstructive and aesthetic surgery, situations requiring breast reconstruction and repair are not limited to the results of cancer surgery. In fact, it is necessary to divide the causes into two: congenital and acquired . The most typical example is the Poland sequence, which is not very rare among congenital causes and is accompanied by a deficiency in the development process of the breast muscles, rib cage, shoulder, arm, forearm, hand and fingers, as well as the development process of the breast . In these patients, the nipple and surrounding brown tissue called areola, breast tissue, or various combinations of these may not have developed. Since rib cage and chest muscle problems may also accompany it, care should be taken in planning the creation of the breast. In these patients, it is necessary to first correct the rib cage deformity and then decide how the breast will be formed. The Poland sequence causes problems not only in women but also in men. In men, it is possible to make near-ideal repairs by performing a three-dimensional volume analysis and imitating the chest muscle with custom-made silicone prostheses.
Image note: Chest wall deformity and absence of breast in a female patient with Poland syndrome.
Acquired causes of breast absence include partial or complete removal of the breast due to breast cancer, and breast tissue loss due to burns or trauma. The possible mechanism is that the breast cannot find a space to develop in adolescence due to skin hardness and tissue insufficiency in burns suffered during childhood. Since the breast is partially or completely removed in cancer surgeries, the patient must be evaluated in detail and both the missing breast skin and breast tissue must be replaced.
Do I have to wait a long time for my breast to be reconstructed after cancer surgery?
Breast reconstruction or repair can be performed together with cancer surgery. While breast cancer is a problem that wears women out psychologically, it is very important for the patient to wake up from the surgery feeling as if her breast has not been removed. Plastic surgery is with the patient to ensure this.
In breast reconstruction, two types of repair can be mentioned in cases of cancer-related losses. One of these is the surgeries called simultaneous breast repair and reconstruction , in which the breast is replaced in the session where the breast is removed, and the other is the surgeries called late-stage breast repair and reconstruction . In this last case, the patient may apply for breast reconstruction much later than the first surgery, either with the guidance of the general surgeon who performed the cancer surgery or because the patient changed her mind years later, saying "I want to get rid of cancer as soon as possible, but it would be okay if I didn't have a breast".
I am hesitant about making breasts with silicone. There were doctors who told me that my body would reject silicone in the future and that it would prevent my cancer treatment. Is it okay if I have my breasts made with my own tissue?
There are basically two types of methods for breast reconstruction and repair (MYO). The first is MYO with artificial silicone implants (heterologous) , and the other is MYO with the person's own tissue (autologous)
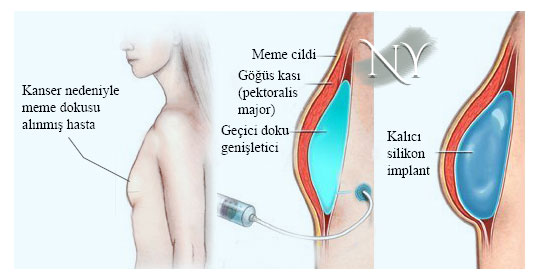
. MYO with silicone implants is generally performed after tumor removal in simultaneous MYO surgeries. If the breast skin and/or nipple can be preserved during surgery (nipple-sparing mastectomy), treatment is provided by placing a silicone implant of appropriate consistency directly under the skin or under the chest muscle. If the skin and nipple are removed during cancer surgery, a tissue expander is placed under the chest muscle, which is hollow and inflated over time after the surgery, allowing us to gain skin. In the meantime, if the patient is to undergo radiotherapy or chemotherapy, the tissue expander is inflated intermittently until the end of that process. When the targeted volume is achieved , a permanent silicone gel implant is placed with a second surgery .
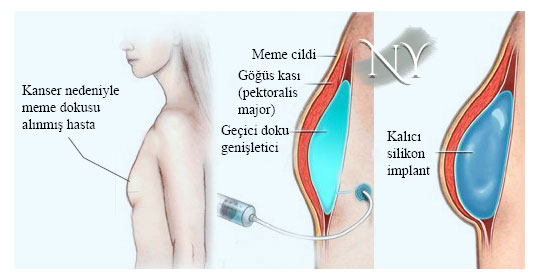
Image note: Breast reconstruction with a silicone implant. First, the skin and the underlying chest muscle are expanded with a temporary tissue expander, then a permanent implant is placed and the nipple and areola are made.
After any foreign substance, including silicone, is ingested into the body, the body detects it and creates an immune response. The end point of this response is the surrounding of the foreign body with a connective tissue shell called capsule. In patients who will undergo radiotherapy, there is a thickening and hardening of the capsule tissue, and a condition called capsule contracture, which causes pain by stretching the soft tissue with the implant, may be encountered. In this case, either the implant must be replaced and the capsule removed, or the repair must be performed with the patient's own tissue. We also have patients who have survived breast reconstruction with silicone implants for many years without any problems. Therefore, in simultaneous MYO surgeries, it may be more logical to prefer repair with implants rather than leaving the operating table without a breast. My patients have the chance to regain their breasts with their own tissue at any time in their lives. The same is true for MYO with silicone implants in patients who are not satisfied with the breast volume created with their own tissue.
The use of your own tissue is also possible in MYO surgeries simultaneously with cancer surgery. However, I do not recommend wasting your own tissue in patients who will receive radiotherapy, especially if the skin and nipple will be removed. In some of our patients, we can use the latissimus dorsi muscle , which is the wide muscle of the back, by turning it to the front in order to fully cover the implant . In patients with weak and smaller breasts where the muscle volume is sufficient, we can reconstruct the semen by using only this muscle and the skin on it.
It was said that after breast construction with silicone, the size of the breast may be different from the other. What is the reason of this?
Surgeries in which the breast is reconstructed, whether with an implant or its own tissue, generally cannot provide the same volume as the opposite breast. Especially in sagging breasts, while creating the new breast on the cancerous side, we can move the nipple and areola level to the point where it should be anatomically and reduce the opposite breast in another session. We also perform lift surgery. In patients who have both breasts removed at the same time due to cancer, it is more possible to fit the two sides together.
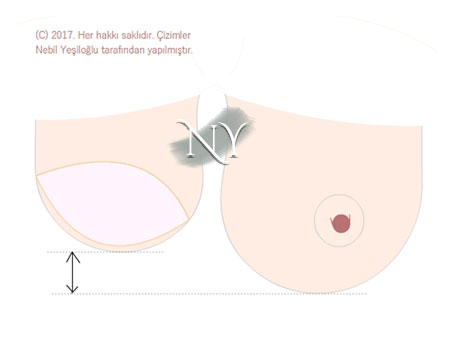
Image note: After breast creation with silicone or your own tissue, your new breast may be a different size and color from the other. Size differences are eliminated by lifting or reducing the opposite breast in other sessions.
Is nipple creation surgery painful?
Creation of the nipple can be performed either in the same session as the breast tissue or in a later session. For this purpose, small tissues called flaps are prepared in the area to be created and a nipple cylinder is created. In patients with preserved skin, regional anesthesia may be necessary as sensory return may rarely occur. If the breast is created with your own tissue, it can be performed with a painless surgery since there will be no sensation. In the construction of the areola, which is the brown tissue around the nipple, either tattooing or skin patches taken from areas with darker skin on the body must be placed in the areola area. The skin patch procedure requires numbing the area where the patch is removed.
When breast tissue is created from my hip, will there be a noticeable scar on my hip? Can I sit comfortably after the surgery?
In order to create the breast with the person's own tissue, it is used as a shadow-receiving area in many parts of the body, including the abdomen, back, hips and even the area above the knee called the thigh. Here, the patient and the physician must make a joint decision.
In abdominal breast reconstruction surgeries, the part of the abdomen below the belly button and sometimesthe flat abdominal muscle called rectus just below it are moved to the breast area. In this surgery, either the tissue is moved to the area prepared above without interrupting the connection at the upper end of the muscle, or the tissue is released by performing vascular work and the tissue's vein is connected to the recipient veins in the rib cage or under the armpit to provide nutrition to the tissue (free tissue transplantation, DIEP, SIEA, TRAM flaps) . In patients who are overweight and have a lot of sagging in the abdomen, it is more reliable to transport the tissue freely. In suitable patients, it is possible to transport abdominal tissue using free tissue transplantation and microsurgery without wasting any of the flat abdominal muscle.
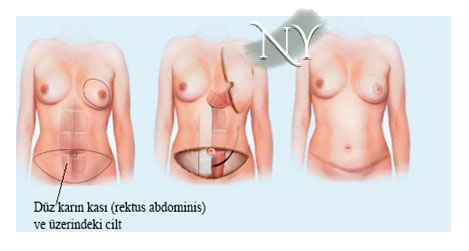
Image note: Reconstruction of the breast with abdominal tissue. This surgery leaves a scar hidden in the bikini line. There will also be a scar around the belly button. The patient also undergoes tummy tuck (abdominoplasty) surgery.
In surgeries to reconstruct the broad muscle of the back (latissimus dorsi) and the breast, a horizontal and sometimes diagonal scar may remain on the back. The latissimus muscle is lifted, including the skin on it, leaving the armpit connection intact, rotated to the front of the rib cage and stitched there. It may also be necessary to place a silicone implant underneath in overweight patients.
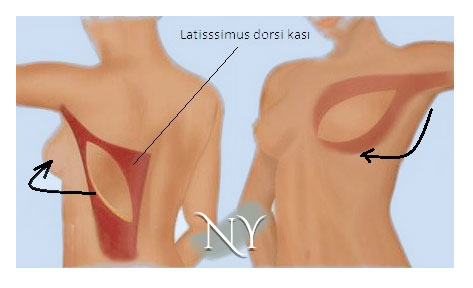
Image note: Creating breast tissue with the large back muscle (latissimus dorsi) and the skin on it. The midline connections of the muscle are separated and rotated to the front. If the patient is thin, it is sufficient for breast volume. It may be necessary to place a silicone implant underneath in overweight patients.
It is also possible to create breasts from the upper and lower folds in the hip area . In these surgeries,free tissue transfer is applied using the microsurgical method (SGAP, IGAP flaps). It is recommended that the patient not apply excessive load and pressure to the hip area for an average of 20 days after the surgery. This type of surgery will leave a scar on the upper or lower fold of the hip.
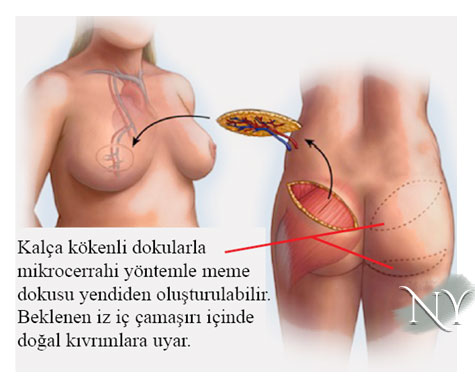 Image note: Reconstruction of the breast with hip tissue.
Image note: Reconstruction of the breast with hip tissue.
Is breast reconstruction surgery risky?
MYO surgeries require the patient to operate under general anesthesia (narcosis). This requires that the general risks of anesthesia be accepted by the patient. Especially when choosing patients with additional internal risks (diabetes, heart failure, thyroid gland diseases, hypertension, etc.), options where the surgery duration is not too long can be preferred together with the physician.
The risks or problems that surgery may cause are wound site infections and healing problems (especially in those receiving high dose radiotherapy), complete or partial loss of tissue in microsurgery-based repairs where autologous tissues are transferred with vascular anastomosis , blood accumulation under the tissue (hematoma), possible wound in the area where tissue is taken. problems can be considered. One of the main risks of microsurgical surgeries is tissue loss that occurs when the vessels feeding the tissue stop working and not giving blood. Especially in people diagnosed with atherosclerotic vascular disease ("arteriosclerosis"), such methods may pose risks and other techniques may be considered.
In patients where autologous tissue is used, especially in patients where the large back muscle (latissimus dorsi) is used for repair, there may be a transparent-light red fluid accumulation called "seroma" in the area where the tissue is taken. This fluid may occur either when the accumulated blood is dissolved by the body and becomes transparent, or it may occur due to regional fat tissue loss. In this case, it may be necessary to re-place a drain in the area and sometimes even surgically open the operating area, clean the area where fluid has accumulated, and stick it to the abdominal wall with stitches.
In patients using implants, problems such as infection, discharge, protrusion or displacement of the implant may occur in the area where the implant is placed, and problems such as tissue tension and pain due to the formation of the connective tissue "armor" called "capsule".
In patients where back muscle and silicone implants are used together, implant displacements or disturbing muscle twitches may sometimes be observed due to involuntary contractions of the muscle. However, in some studies in these patients, although the problem is solved by denervation of the muscle (cutting the nerve leading to the muscle by ligating), this may lead to a decrease in muscle volume and the implant to become palpable. It is possible to solve the problem temporarily by injecting botulinum toxin-A (Botox, Dysport and others) into this nerve.
In autologous breast repairs performed using abdominal muscle (TRAM flap technique) , the possibility of hernia (herniation) in the abdominal area is not low. Herniation rates of around 30-45% have been reported in different surgery series. The treatment of these hernias is surgery. Strengthening is done by placing a special mesh layer in the area where the abdominal muscle is removed. Even if this strengthening is done in the first surgery, the risk of hernia formation is not completely eliminated and the area may need to be opened and rearranged if necessary. Please pay attention to walking and posture recommendations, corset use, and weight lifting restrictions after abdominal tissue-related surgeries.
Resources that our patients can read ( you can visit the portal www.pubmed.com )
- Gümüş AB, Psychosocial problems and supportive interventions in breast cancer. Breast Health Journal 2006 Volume: 2 Issue: 3 Page 108-114
- Juhl AA, Christensen S, Zachariae R, Damsgaard TE. Unilateral breast reconstruction after mastectomy - patient satisfaction, aesthetic outcome and quality of life. Acta Oncol. 2017 Feb;56(2):225-231. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2016.1266087. Epub 2017 Jan 13.
- Zhong T, Hu J, Bagher S, Vo A, OʼNeill AC, Butler K, Novak CB, Hofer SO, Metcalfe KA. A Comparison of Psychological Response, Body Image, Sexuality, and Quality of Life between Immediate and Delayed Autologous Tissue Breast Reconstruction: A Prospective Long-Term Outcome Study.
- de Raaff CA, Derks EA, Torensma B, Honig A, Vrouenraets BC. Breast reconstruction after mastectomy: does it decrease depression at the long-term? Gland Surg. 2016 Aug;5(4):377-84. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016 Oct;138(4):772-80.
- Zdenkowski N, Butow P, Tesson S, Boyle F. A systematic review of decision aids for patients making a decision about treatment for early breast cancer. Breast. 2016 Apr;26:31-45.
"Health is the most important thing you have in life!"
Contact us now to schedule an appointment.